Arachnoid Cyst: An Unusual Cause for Increased Alkaline Phosphatase
PBJ Sanneerappa1, R Gul1, M Nadeem2, N Ramesh1
1. Midland Regional Hospital, Portlaoise, Laois, Ireland.
2. Adelaide and Meath Hospital, Tallaght, Dublin, Ireland.
Sir,
Alkaline phosphatase (AP) is an enzyme most commonly raised in hepatic pathology. However, there are few non hepatic causes such as diseases of bone, kidney and intestinal mucosa. In this case, we observed an association between arachnoid cyst situated close to skull vault and elevated alkaline phosphatase. To our knowledge, this association has not been observed in previous studies.
A two-and-a-half-year old girl presented with a slight bulge in the left side of her head noticed by her mum 2 days prior to presentation. No history of trauma was reported. Developmental milestones were appropriate for her age. Systemic examination including neurological and musculoskeletal examination was unremarkable.
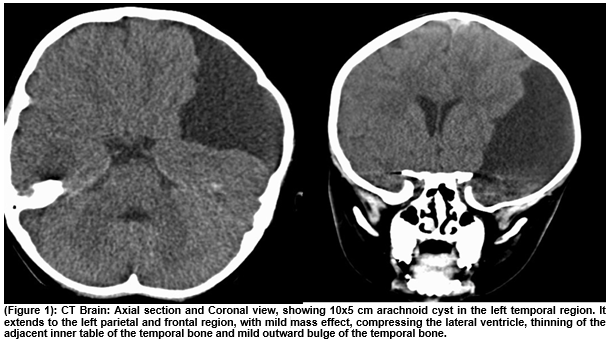
Apart from elevated serum AP (2843 U/L), blood tests including full blood count, Urea and electrolytes, bone profile and liver function tests, lactate dehydrogenase and vitamin D were reported normal. A minimal prominence in left temporal and parietal bone was showed in skull radiograph. CT scan of the head was performed which was abnormal (Figure 1). Chest X ray and abdominal ultrasound were reported normal. In this case, we highlight that arachnoid cyst situated close to skull vault can be one of the causes for elevated alkaline phosphatase.
Elevated serum AP is frequently seen in clinical practice as it is present in multiple organs such as liver, bone, intestine, kidney, placenta and leucocytes, for example 1,2, with a highest concentration being observed in liver and bone. However, it is generally attributed to either liver or bone diseases2. In scenarios where both AP and Gamma Glutamyl Transpeptidase (GGT) values are elevated, hepatic disorders have to be excluded1. Alkaline phosphatise is also an acute phase reactant, similar to ferritin.
(Figure 1): CT Brain: Axial section and Coronal view, showing 10x5cm arachnoid cyst in the left temporal region. It extends to the left parietal and frontal region, with mild mass effect, compressing the lateral ventricle, thinning of the adjacent inner table of the temporal bone and mild outward bulge of the temporal bone.
To conclude, in this case report we vividly demonstrate that a huge arachnoid cyst adjacent to the temporal and parietal part of the left side of the skull can be one of the causes of isolated raised alkaline phosphatase in a well child with normal development.
Correspondence:
Phani Bhushan Jeerigehalli Sanneerappa
0872140923
References
- Giannini EG, Testa R, Savarino V. Liver enzyme alteration: a guide for clinicians. CMAJ. 2005; 172(3):367-79.
- Asma Siddique, Kris V. Kowdley. Approach to A Patient With Elevated Serum Alkaline Phosphatase. Clin Liver Dis. 2012; 16(2):199–229.
P475