This Month’s IMJ:
Cycling injuries presenting to an Irish emergency department:
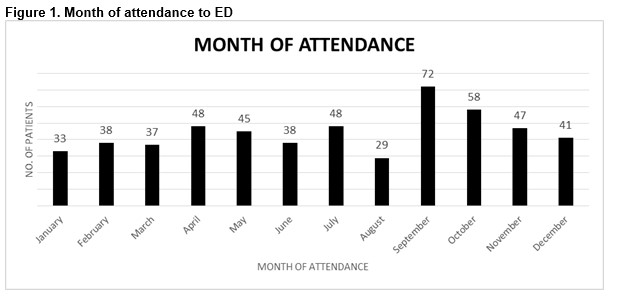
Foley et al documented 534 cycling related injuries in a 12 month period. 40 cyclists needed in-patient admission and 6 were transferred to intensive care. The common causes of injury were 244 (fall from the bike), 79 (collision with a motor vehicle), 42 (collision with a pedestrian).
p419
_________________________________________________________
A Study of the Patients Admitted to the Clinical Decision Unit Over One Year
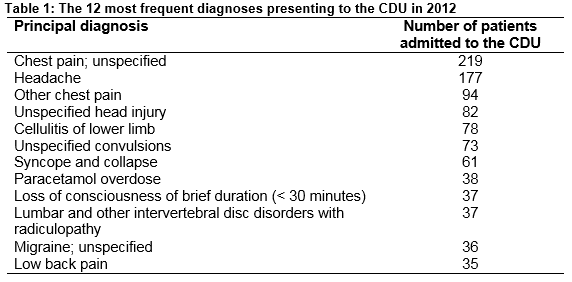
O’Shea et al describe the activity and efficacy of a CDU. A total of 2,307 patients were assessed. The mean length of stay was 29 hours. The authors calculate that the CDU could save as much as €2 million annually.
p424
_________________________________________________________
Botulinum Toxin in the management of sialorrhoea in acquired brain injury:
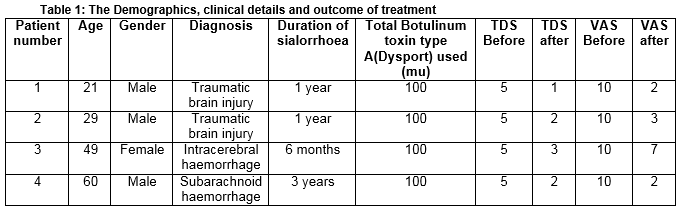
Carroll and McGlone describe the use of Botulinum toxin medication for sialorrhoea in patients with acquired brain injury. In all cases it significantly reduced drooling.
p425
_________________________________________________________
Type 1 Tyrosinaemia:
Mannion et al report 3 cases of Tyrosinaemia type 1. Hypoglycaemia is the common presenting feature. Liver failure is an important complication. Since the introduction of Nitisinone medication the numbers requiring liver transplantation has reduced significantly.
p426
_________________________________________________________
Management of Epistaxis- A single centre experience and economic considerations:
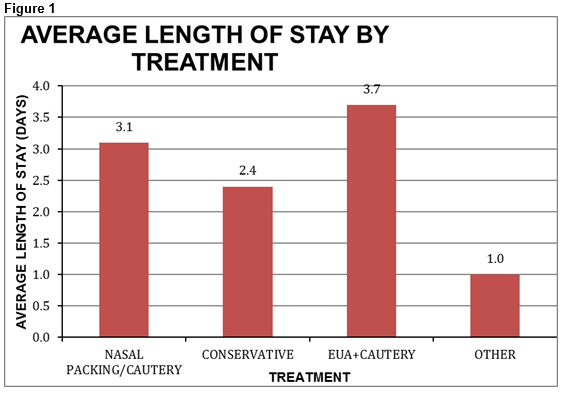
Keane et al report that 434 patients were admitted with epistaxis over a 4 year period. 362 were managed conservatively and 15 required surgery.
p427
_________________________________________________________
The prolonged neonatal admission: implications for our national children’s hospital:
McGlacken-Byrne et al describe the patterns of prolonged hospital stay for young infants.
p428